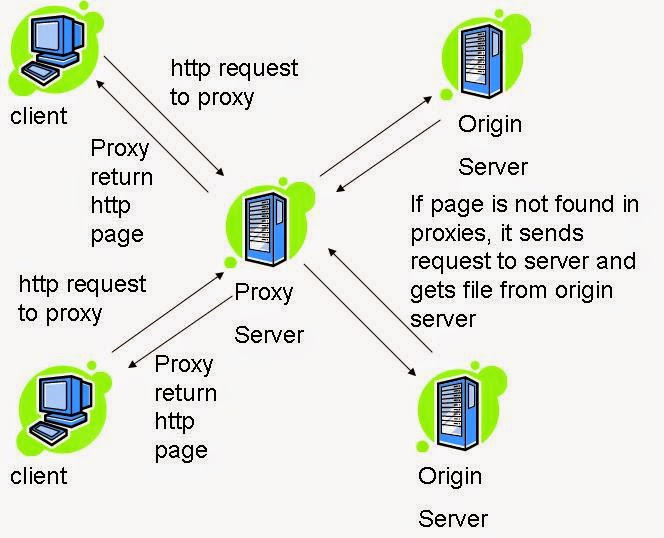
A proxy server is a server (a computer system or an application) that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients
seeking resources from other servers. A client connects to the proxy
server, requesting some service, such as a file, connection, web page,
or other resource available from a different server and the proxy server
evaluates the request as a way to simplify and control its complexity.
Proxies were invented to add structure and encapsulation to distributed
systems.Today, most proxies are web proxies, facilitating access to content on the World Wide Web and providing anonymity.Continue Reading...
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia